Nálezy nejenom s detektorem v západní Evropě
Subcategories
Archeologické nálezy pomocí detektorů kovů v západní Evropě
Západní Evropa, zahrnující státy jako Francii, Německo, Nizozemsko, Belgii a Velkou Británii, je regionem bohatým na archeologické nálezy pokrývající dlouhé období lidské historie. Díky rozmanitým kulturním a politickým vlivům, od doby bronzové přes římskou éru až po středověk, je tento region pokladnicí historických artefaktů. Detektory kovů zde sehrály klíčovou roli při odhalování důležitých nálezů, které poskytují unikátní pohled na život našich předků.
Nejvýznamnější typy nálezů:
-
Poklady z doby bronzové a železné:
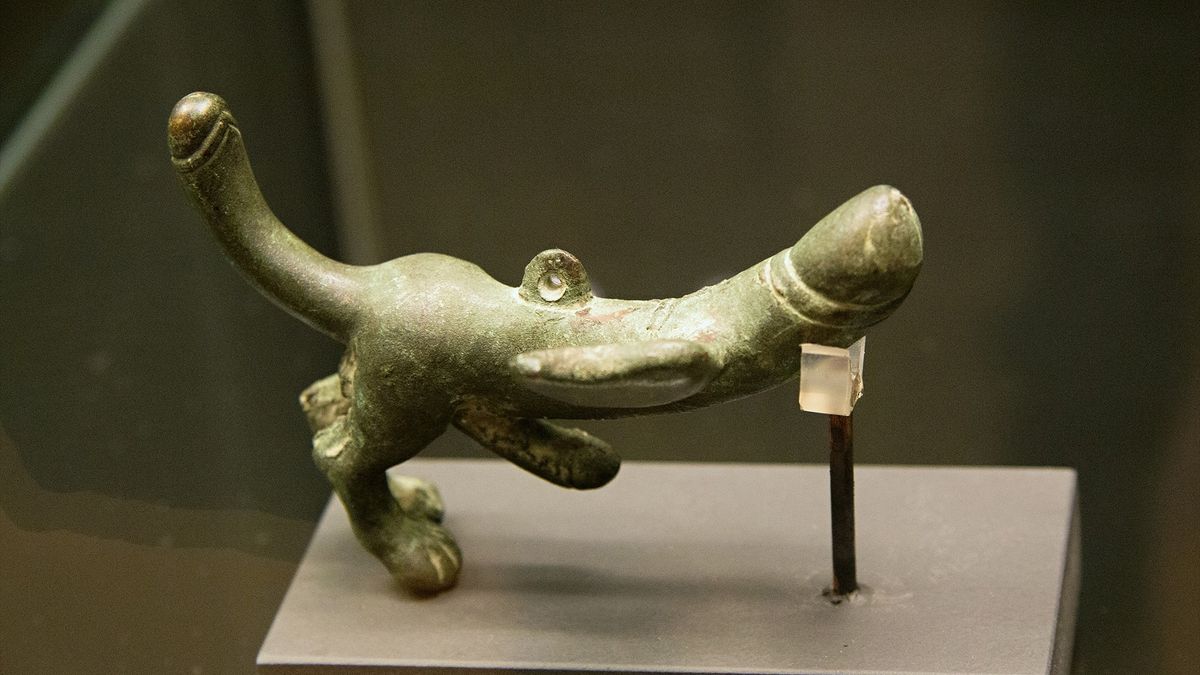
- Západní Evropa je známá bohatými nalezišti z doby bronzové, včetně dep ozdob, zbraní a nástrojů. Depozity obsahují předměty jako bronzové sekery, meče a ozdoby, které byly často obětinami bohům nebo bezpečně uschovány.
- Nálezy z doby železné zahrnují keltské mince, šperky a rituální předměty, zejména v oblasti Francie a Británie.
-
Římské nálezy:
- Římské mince, nástroje, zbraně a keramika jsou častými nálezy v regionech ovládaných Římskou říší.
- Významnými nálezy jsou i římské cesty, opevnění a vily, které se nacházejí v oblastech dnešního Německa, Francie a Británie.
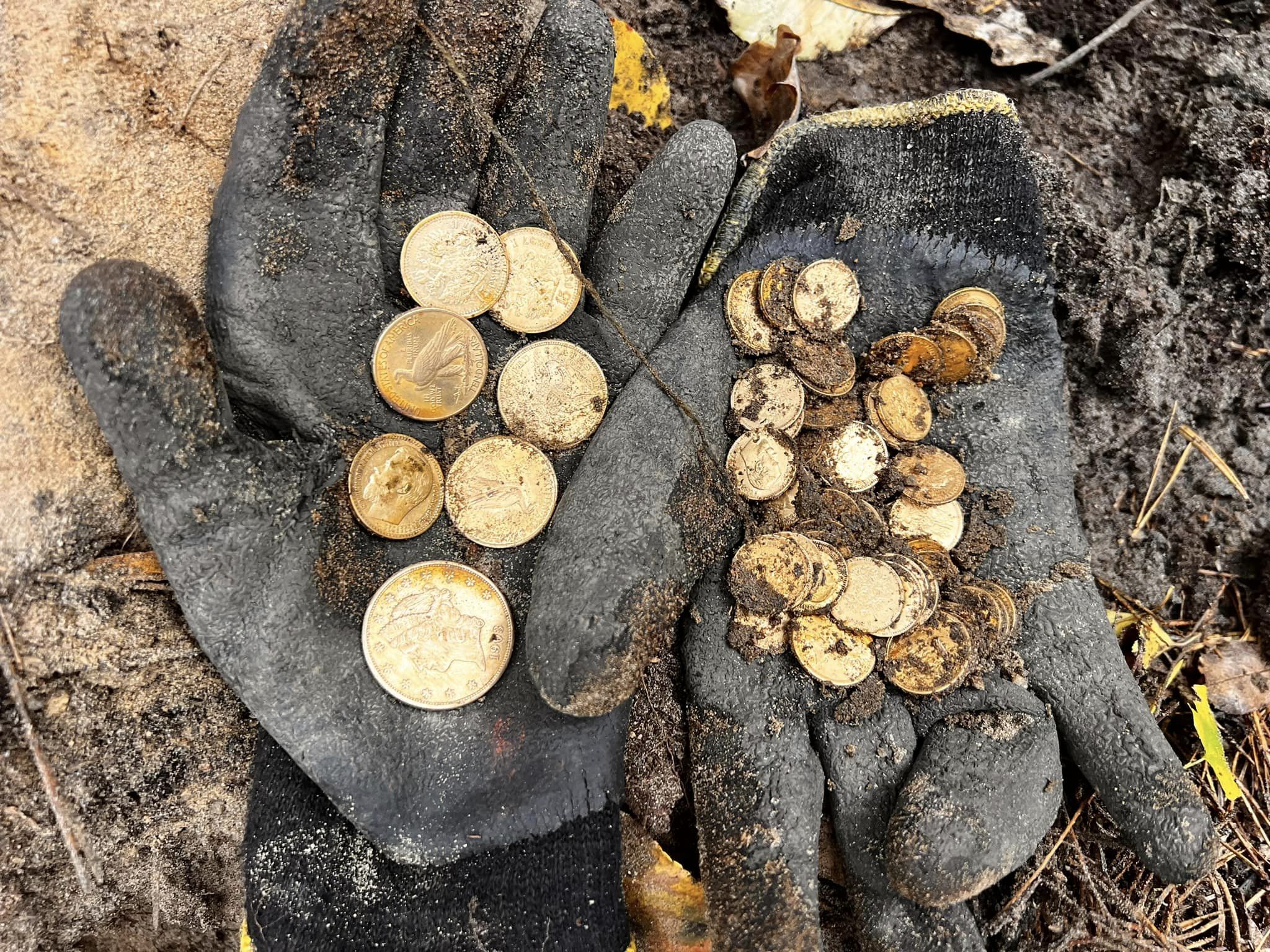
- Detektory často odhalují římské poklady ukryté během nepokojů, například zlaté a stříbrné mince (aureus, denarius) nebo šperky.
-
Středověké nálezy:
- Západní Evropa byla centrem středověké kultury, což se odráží v počtu nálezů z tohoto období. Mezi nejcennější patří mince, ozdoby a zbraně.
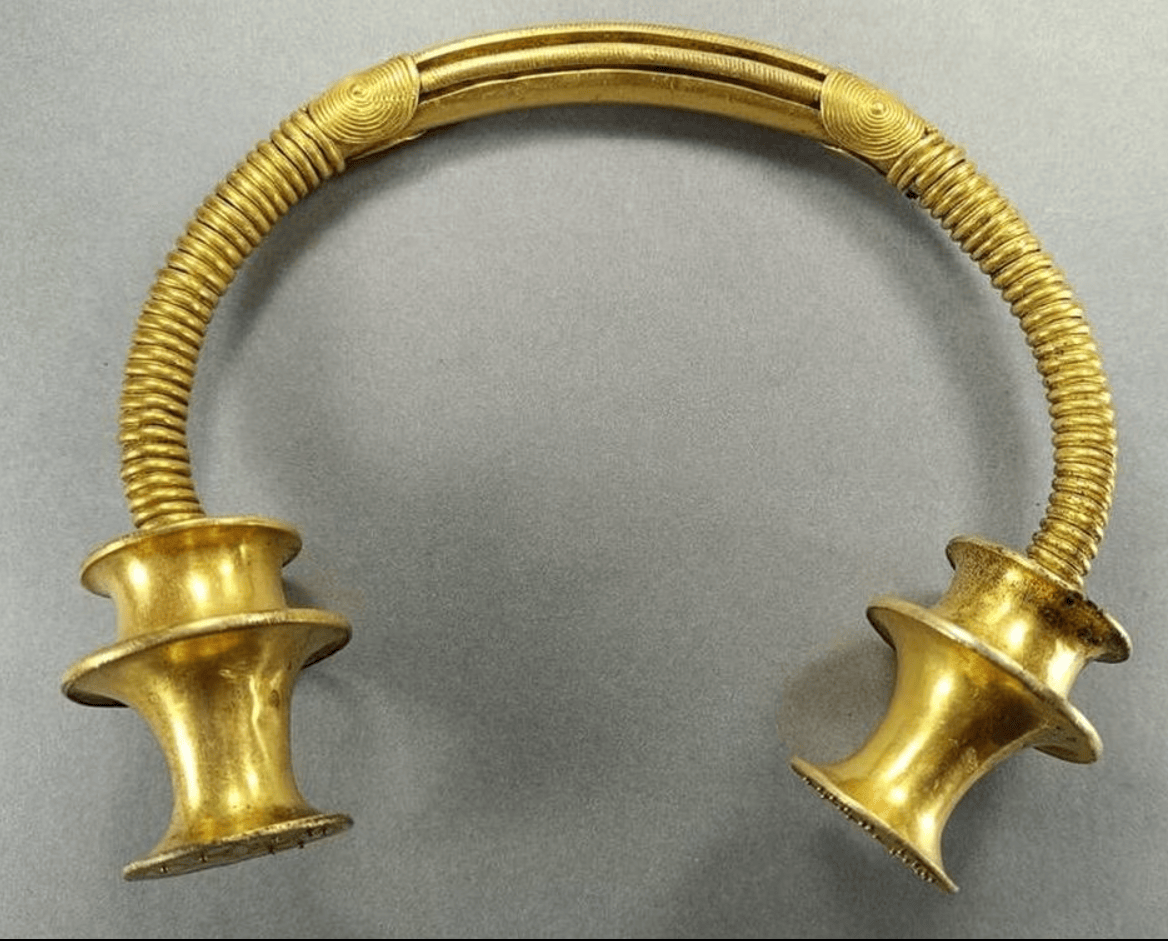
- Poklady anglosaské a merovejské kultury, například šperky zdobené emaily a drahými kameny, jsou významné zejména ve Velké Británii a Francii.
- Německo a Nizozemsko často přinášejí nálezy spojené s raně středověkými hradišti a tržními místy.
-
Renesanční a novověké nálezy:
- Mince a šperky z období renesance, často bohatě zdobené a vysoce kvalitní.
- Nálezy z období koloniální expanze, například obchodní zboží, pečetidla a platidla.
Významné lokality:
-
Británie:
- Jedno z nejbohatších míst pro hledače s detektory kovů. Nálezy jako Sutton Hoo (pohřebiště anglosaského krále) nebo Staffordshirský poklad svědčí o významu této oblasti.
- Římské osady jako Colchester nebo Bath jsou bohatými nalezišti artefaktů.
-
Francie:
- Keltské nálezy, například mince a šperky z oppid (keltských opevněných sídlišť) jako Bibracte.
- Římské lokality jako Arles nebo Nîmes, bohaté na mince a keramiku.
-
Německo:
- Nálezy spojené s Římskou říší, zejména z bojiště v Teutoburském lese, kde se našly zbraně a vojenské vybavení.
- Středověké nálezy spojené s obchodními stezkami a městy Hanza.
-
Nizozemsko a Belgie:
- Oblasti, kde byly odhaleny keltské a římské poklady, zejména v povodí Rýna a Maasy.
- Množství mincí, šperků a obchodních artefaktů z doby středověku.
Role detektorů kovů v objevech:
Detektory kovů hrají klíčovou roli při objevování historických artefaktů v západní Evropě. Moderní technologie umožňují lokalizaci nálezů na polích, v lesích i na archeologických lokalitách. Hledači často spolupracují s archeology, což přináší významné příspěvky k pochopení historie regionu.
Západní Evropa je díky své bohaté historii jednou z nejzajímavějších oblastí pro hledače s detektory kovů, jejichž objevy stále rozšiřují naše poznání o dávných civilizacích a kulturním vývoji.